Roof vs. Ground-Mounted Systems
Roof-Mounted Panels:
- Pros: Roof-mounted solar panels are often more practical for residential installations. They save ground space, use existing structures, and are less susceptible to vandalism.
- Cons: Roof conditions, such as age, material, and structural integrity, can affect the feasibility of installation. Additionally, roof-mounted systems may be limited by the available surface area and orientation.
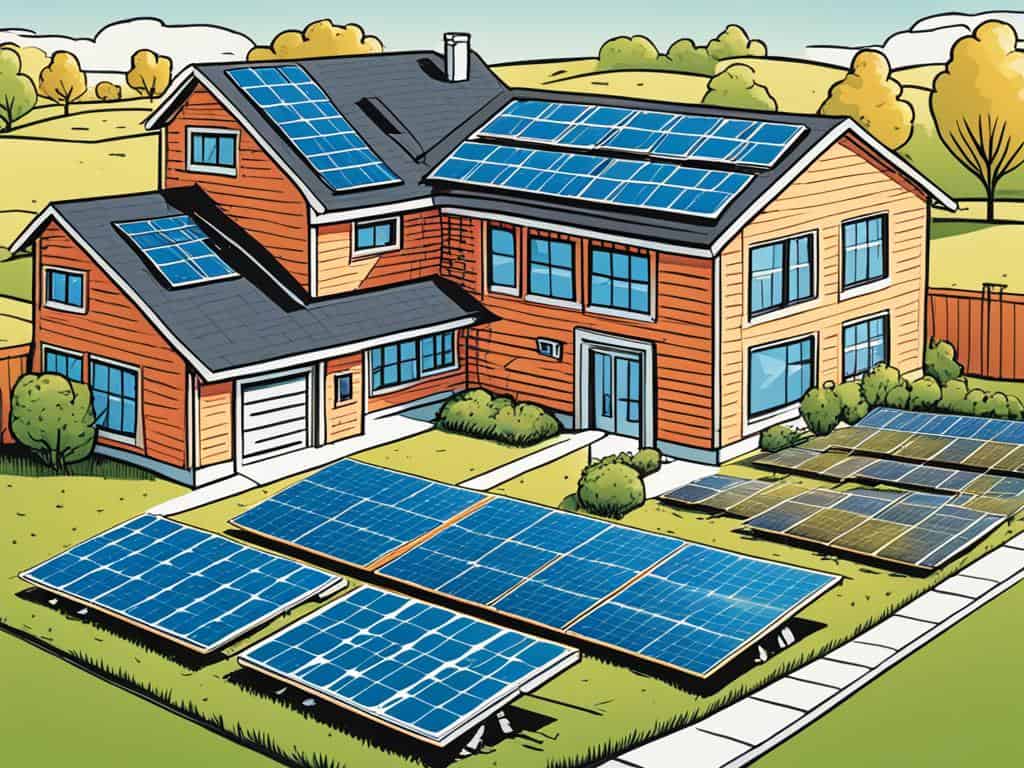
Ground-Mounted Panels:
- Pros: Ground-mounted systems offer greater flexibility in panel orientation and tilt angle. They can be positioned for optimal solar exposure and are easier to maintain and expand.
- Cons: These systems require dedicated ground space and may be subject to local zoning regulations. They can also be more vulnerable to damage or interference.
Local Climate and Weather Conditions

Climate Impact:
- Sunlight Hours: The average number of sunlight hours in a location plays a significant role in solar panel efficiency. Areas with more sunlight will naturally generate more energy.
- Temperature Effects: Solar panels are sensitive to temperature. While they function in all climates, high temperatures can reduce their efficiency. Proper ventilation and choosing panels with high-temperature tolerance can mitigate this issue.
Weather Considerations:
- Snow and Ice: In regions with heavy snowfall, installing panels at a steeper angle can help shed snow, preventing energy production losses. Regular maintenance and snow removal are also essential.
- Hail and Wind: Ensure panels and mounting systems are designed to withstand local weather conditions, including high winds and hail storms.
